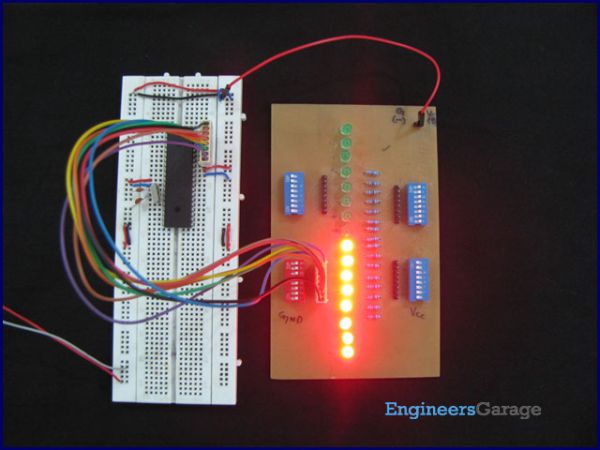
It is necessary to understand basic I/O operations of PIC18F4550 before dealing with its complexities. This article presents a way to take simple output from a PIC microcontroller. This learning would also help in interfacing of external devices with the controller. Here the output from the microcontroller is taken on a set of LEDs which are made to blink in an alternate fashion.
PIC18F4550 has a total of 35 I/O (input-output) pins which are distributed among 5 Ports. The following table shows the names and numbers of I/O pins of these 5 ports:
|
Port Name
|
Number of Pins
|
Pins
|
|
PORTA
|
7
|
RA0-RA6
|
|
PORTB
|
8
|
RB0-RB7
|
|
PORTC
|
7
|
RC0-RC2, RC4-RC7
|
|
PORTD
|
8
|
RD0-RD7
|
|
PORTE
|
4
|
RE0-RE3
|
As opposed to a basic 8051 microcontroller like AT89C51 which has most of the port pins serving single function, the port pins of a PIC microcontroller are multiplexed to serve more than one purpose.
The 35 I/O pins of PIC18F4550 are also multiplexed with one or more alternative functions of controller’s various peripherals. Each Port of a PIC microcontroller corresponds to three 8-bit registers which should be configured to use the Port for general I/O purpose. These registers are:
1. TRISx: This is a data direction register which sets the direction of each port pin as input or output.
2. PORTx: This register stores the input level of pins (High or Low). When a pin configured as input, the input signal from external source is read from PORTx register.
3. LATx: This is output latch register. The data which has to be sent to external hardware as output is stored in LATx register.
Port Description:
PORTA:
PortA has 7 pins which can be used as both input as well as output pin. The 7th bit is missing from all the three registers. The input and output given to this port are of 8-bit but the 8th bit is internally masked.
|
Bit 7
|
Bit 6
|
Bit 5
|
Bit 4
|
Bit 3
|
Bit 2
|
Bit 1
|
Bit 0
|
|
|
TRISA
|
–
|
TRISA6
|
TRISA5
|
TRISA4
|
TRISA3
|
TRISA2
|
TRISA1
|
TRISA0
|
|
PORTA
|
–
|
RA6
|
RA5
|
RA4
|
RA3
|
RA2
|
RA1
|
RA0
|
|
LATA
|
–
|
LATA6
|
LATA5
|
LATA4
|
LATA3
|
LATA2
|
LATA1
|
LATA0
|
PORTB:
PortB has 8 pins which can all be used for both input and output operation.
|
Bit 7
|
Bit 6
|
Bit 5
|
Bit 4
|
Bit 3
|
Bit 2
|
Bit 1
|
Bit 0
|
|
|
TRISB
|
TRISB7
|
TRISB6
|
TRISB5
|
TRISB4
|
TRISB3
|
TRISB2
|
TRISB1
|
TRISB0
|
|
PORTB
|
RB7
|
RB6
|
RB5
|
RB4
|
RB3
|
RB2
|
RB1
|
RB0
|
|
LATB
|
LATB7
|
LATB6
|
LATB5
|
LATB4
|
LATB3
|
LATB2
|
LATB1
|
LATB0
|
PORTC:
PortC has 7 I/O pins. In PortC, Bit 3 is missing in hardware and Pins 4 & 5 can only be used as input pins. There are no 4th & 5th latch bits in LATC register, so these bits are internally masked during 8-bit write operation on PortC.
For more detail: How to interface LEDs with PIC18F4550 Microcontroller
The post How to interface LEDs with PIC18F4550 Microcontroller appeared first on PIC Microcontroller.